Why you shouldnt be scared of sharks?

Sharks help preserve the fragile balance of ecosystems by keeping other populations under control. They keep healthy populations, too, by feeding on the sickest and weakest of their prey so that the healthy can thrive. To see also : Who is Nathan Fletcher surfer?. Sharks also help protect habitats such as seagrass beds and coral reefs.
Why should people be afraid of sharks? The chances of you being eaten alive by a shark are highly unlikely. You are more likely to die from a dog attack, lightning strike, or car crash. Cancer and heart disease are also much more likely to kill you. The small chances that a shark attack could get us are irrelevant.
Should sharks be afraid of humans?
Most sharks are not dangerous to humans – people are not part of their natural diet. Read also : What are sharks afraid of?. Despite their reputation for fear, sharks rarely attack humans and prefer to eat fish and marine mammals.
Why sharks should be scared of humans?
Indeed, if we kill too many sharks in an effort to catch more fish, this imbalance will eventually cause fish stocks to collapse – and the marine environment to degrade.
Should we fear sharks?
They protect oceanic habitats such as seagrass and coral reefs by feeding on certain grazing species. Without sharks, those habitats would be overgrazed, leading to far more dependent-dependent deaths for survival.
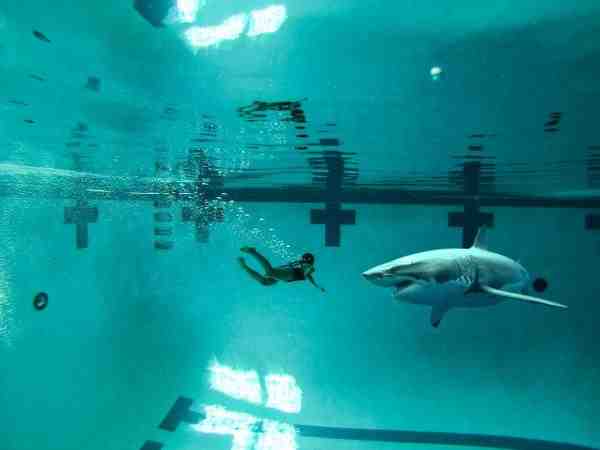
How do I stop being scared of sharks?
One of the best ways to overcome the fear of sharks is to swim with them. Many aquariums offer opportunities for you to swim with sharks. This may interest you : How much does Bethany Hamilton make?. This puts you in a safe, shark-controlled environment so that you can face your fears and begin to dispel the fear that all sharks are killers.
Can sharks sense fear in humans?
Can Sharks Last a Fear? No, they can’t. The sense of smell of a shark is strong, and they can smell everything that interacts with their sensory cell on their nostrils, but that doesn’t include feelings like fear. But you have to remember that sharks don’t just depend on their sense of smell alone.
Is fear of sharks normal?
A study published in 2015 found that 51% of Americans said they were “absolutely terrified” of sharks and 38% of Americans said they were afraid to swim in the ocean because of them, showing that fear is not necessarily based on risk.
What month do most shark attacks happen?

September is the month with the most Shark attacks in Florida (93) 1920-2010.
Which beach has the most shark attacks? New Smyrna Beach, Florida Florida has more shark attacks each year than any other area in the world, according to the International Shark Attack File (ISAF).
Where do most shark attacks occur?
Most shark attacks occur less than 100 feet from the shore mostly around popular beaches in North America (especially Florida and Hawaii), Australia, and South Africa.
Where does the most shark attacks happen?
Which state has the most shark attacks? The states with the most recorded shark attacks ever recorded are Florida, Hawaii, California, and the Carolinas. Florida is known as the “capital of shark attacks in the world” and accounts for more than half of all total shark attacks in the United States each year.
Where are the most shark attacks in the world how many?
The United States once again reported the most attacks and Florida accounted for nearly 40% of unprovoked bites worldwide. Researchers with the International Shark Attack File recorded 73 unprovoked incidents last year, compared to 52 bites in 2020, according to a new report.
What time of year are sharks out?
3. Avoid water at night, dawn, or dusk. Many sharks are most active at this time and are more able to find you than you are to see them.
What time of year do sharks come close to shore?
Sharks are more active at dawn and dusk, choosing these times to hunt their prey near the shore. Due to ingenious adaptation, sharks can maximize the available light to gain an even greater advantage over their prey. Therefore, they choose to hunt when visibility is poor.
What time of year are sharks most active?
Most of the attacks around the world take place between 8.00 am and 6.00 pm and mostly on weekends during the hottest seasons of the year. However, this has nothing to do with shark behavior but rather with human behavior as these are the times when many people are spending time in the water.
What time of year do most shark attacks occur?
Most of the attacks around the world take place between 8.00 am and 6.00 pm and mostly on weekends during the hottest seasons of the year. However, this has nothing to do with shark behavior but rather with human behavior as these are the times when many people are spending time in the water.
Where do shark attacks happen most?
On average, there are 16 shark attacks a year in the United States, with one fatality every two years. According to ISAF, the states in the United States with the most attacks are Florida, Hawaii, California, Texas and Carolinas, although attacks have occurred in almost every coastal state.
What time of day are you most likely to be attacked by a shark?
Shark attacks are more likely to occur at dawn and dusk, precisely when they are more active in search of food. Also, because visibility is limited during the hours of twilight, sharks can mistake you for prey or enemies.
What causes Trypophobia?

What causes trypophobia? The exact cause of tripophobia is unknown, as research in this area is limited. Various causes of tripophobia have been identified, such as honeycomb, bubble wrap, or fruit seeds. Certain patterns, bumps, patterned animals, and imagery can also elicit tripophobic reactions.
How to get trypophobia holes? Common things that can cause tripophobia include:
- Holes or pebbles in concrete.
- Air holes in a slice of bread.
- Patterns in the frost of a cake or pie.
- The head of a lotus flower.
- Holes in an old hockey mask.
- Skin problems such as sores, scars, and spots.
- Spotted animals.
- Shower heads.
What is the reason for trypophobia?
Experts do not know why some people develop trypophobia. One theory is that the brain associates groups of holes with danger. For example, you could associate a pattern of small holes with the skin of a venomous snake or the eyes of a tarantula. Either the holes can remind you of skin diseases or skin rashes.
Is there a cure for trypophobia?
Treatment of Trypophobia Because trypophobia is not a real disorder, there is no established treatment for it. Some studies show that an antidepressant such as sertraline (Zoloft) in combination with a type of speech therapy called cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is helpful. CBT tries to change the negative ideas that cause fear or stress.
Can trypophobia be cured?
Is there a cure for tripophobia? To the extent that trypophobia is a type of anxiety, medications used to treat anxiety can offer relief. But there is no cure, and little research has been done to look for one. Exposure therapy – in which patients are gradually exposed to pictures or unpleasant situations – can be helpful.
How do you get rid of trypophobia?
Because trypophobia is not a true disorder, there is no established treatment for it. Some studies show that an antidepressant such as sertraline (Zoloft) in combination with a type of speech therapy called cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is helpful. CBT tries to change the negative ideas that cause fear or stress.
Is trypophobia a mental disorder?
Diagnosis and Testing The American Psychiatric Association (APA) does not recognize trypophobia as a disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). This may be because the condition is often uncomfortable but not debilitating.
Is trypophobia a mental illness?
Trypophobia is not classified as a mental disorder. However, it may meet the criteria for phobia if the sight of collected patterns causes sudden fear and anxiety to the extent that it causes noticeable suffering or impairment. There is debate as to whether trypophobia meets the clinical definition of a specific phobia.
Can trypophobia be serious?
While not listed in the DSM-5, tripophobia falls under the broad classification of specific phobias as long as the symptoms are persistent, excessive, and lead to significant impairment or suffering.
Does everyone suffer from trypophobia?
Tripophobia is widely documented by Internet sufferers and, in one study, Cole and Wilkins found that about 16% of participants reported tripophobic reactions.
What is a Selachophobia?

selachophobia (uncountable) Unreasonable fear or dislike of sharks.
How do I know if I have galeophobia? Symptoms of galeophobia When seen by a shark, either on the beach or in an aquarium or on a boat, galeophobes may experience deep mental distress, shortness of breath, tremor, nausea, and dizziness. In common, they close their eyes, cry, cry, and try to escape the situation.
What is the phobia of Megalodons?
Fear of Shark Phobia – Galeophobia or Selachophobia.
What causes galeophobia?
Some situations naturally trigger these fears, for example, traumatic events involving attacks by predators and sharks. The extreme response to the presence, reference to, or thought of a shark is a natural reaction of the human body to danger. A simple picture of a scary shark can be the cause of a panic attack.
What does Selachophobia mean?
selachophobia â € ‹Definitions and Synonyms â €‹ noun. DEFINITIONS1. 1. Strong dislike or fear of sharks.
How do you overcome galeophobia?
One of the best ways to deal with galeophobia is precisely to face and meet the “evil” creature in person. Many water parks provide programs that allow people to swim with sharks without being eaten alive. The goal is to overcome fear by challenging it, face to face, at arm’s length.
Is a fear of sharks irrational?
Fear of sharks, or galeophobia, is not unreasonable, says marine biologist Blake Chapman, a shark expert at the University of Queensland in Australia. Simply put, predatory fish are awesome.
What is the fear of being eaten by a shark called?
Overcoming and Treating the Fear of the Shark One of the best ways to deal with galeophobia is precisely to face and meet the “evil” creature in person. Many water parks provide programs that allow people to swim with sharks without being eaten alive.
What is Megalohydrothalassophobia?
megalohydrothalassophobia (fear of creatures or large underwater objects) cymophobia (fear of the waves) nyctophobia (fear of the dark) antlophobia (fear of the flood)
What is the fear of Ichthyophobia?
Fear of fish or ichthyophobia ranges from cultural phenomena such as fear of eating fish, fear of touching raw fish, or fear of dead fish, to irrational fear (specific phobia).
What is the Glossophobia?

Glossophobia, or fear of public speaking, is remarkably common. In fact, some experts estimate that up to 77% of the population has some level of anxiety about public speaking.
What is the definition of glossophobia? : Fear of public speaking In anticipation of public speaking, a person with glossophobia may experience dry mouth, a weak voice, and uncontrollable body shaking. ” Robert Malone.
What is Megalophobia?
Megalophobia is a type of anxiety disorder in which a person experiences intense fear of large objects. A person with megalophobia experiences severe fear and anxiety when thinking or being around large objects such as large buildings, statues, animals and vehicles.
What is Tomophobia?
Tomophobia refers to fear or anxiety caused by the following surgical procedures and / or medical interventions.
Is megalophobia common?
Megalophobia Pictures and Videos to Test Your Fear of Large Objects. Megalophobia is common among many people, but it can be felt and experienced differently. For example, some may just be afraid of large animals such as elephants and whales, while others may be afraid of specifically man-made objects.
What is glossophobia in public speaking?
Glossophobia, or fear of public speaking, is remarkably common. In fact, some experts estimate that up to 77% of the population has some level of anxiety about public speaking. 1ï »¿Of course, many people are able to manage and control fear.
What does glossophobia feel like?
Symptoms of glossophobia include: High stress, anxiety, and panic when people are asked to speak in front of large or small groups. The person fears that his or her performance will lead to negative judgment or evaluation of people in the audience, and this reaction will lead to embarrassment or humiliation.
What are some examples of glossophobia?
Here are some examples of glossophobia: Musicians, actresses and actors performing in front of large crowds. Business people make presentations to their team. Call a friend or colleague about something. Children are afraid to be asked a question by their teacher.
What causes glossophobia?
The specific causes of glossophobia often vary from person to person. The most common cause, however, is the anticipation of the presentation in front of an audience. Additional triggers may include social interactions, starting a new job, or going to school.
Is glossophobia mental illness?
Glossophobia is not a dangerous disease or a chronic condition. It is the medical term for the fear of public speaking. And it affects as many as four out of 10 Americans. For those affected, speaking in front of a group can lead to feelings of discomfort and anxiety.
Can glossophobia be cured?
Psychotherapy. Many people are able to overcome their glossophobia with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). Working with a therapist can help you identify the root cause of your anxiety. For example, you may find that you are more afraid of ridicule than of speaking because you have been served as a child.
Is it OK to pee in the ocean?
Peeing in the ocean is totally good, but don’t paint in protected areas like reefs or smaller bodies of water, especially swimming pools.
Does peeing in the ocean attract sharks? It’s not Chlorine Turning Your Eyes Red in the Swimming Poolâ € ”It’s a Pee. That’s just not true. We understand where the myth comes from.
How common is pee in the ocean?
“Two-thirds of people (62 percent) admit to pee in the water on the beach, and of those, nearly half (48 percent) say they’ve done it more than once,” according to the sponsored survey. from the Charmin Relief Project, which P&G described as a program designed to bring consumers a better bathroom experience.
Does pee affect the ocean?
It is nitrogen (found in urine) that causes algae to grow, and this is detrimental to coral. Experts also say that drug chemicals in the human body passed into the sea with urine can damage coral reefs by altering the balance of germs.
Is it normal to pee in the ocean?
Feel free to pee in the ocean and go back to worrying about more important things like that shark just behind you. Oh, and we have to mention this. Peeing in the ocean is totally good, but don’t paint in protected areas like reefs or smaller bodies of water, especially swimming pools.
Can you get an infection from peeing in the ocean?
yes, it can feasibly die from cyanogen chloride poisoning from chlorinated water and pee. There are many worse things in the pool. The chemicals themselves send 5000 people to the ER every year. The swimming pool water is also loaded with nasty bacteria.
Does sea water cause infection?
You can get some infections from contaminated ocean water. There are some germs that can live in the ocean and cause infection. Some of the infections you can get from swallowing contaminated ocean water include cryptosporidiosis, shigellosis, and E. coli.
What happens if you pee in the sea?
In general, peeing in the ocean is totally good, says the ACS – and can even be beneficial to marine life, as the nitrogen in urea combines with water to produce ammonium, which feeds ocean plants.
What happens if you pee in sea?
In general, peeing in the ocean is totally good, says the ACS – and can even be beneficial to marine life, as the nitrogen in urea combines with water to produce ammonium, which feeds ocean plants.
Why should you not wee in the sea?
When urinating in the sea is a problem It is nitrogen (found in the urine) that causes algae to grow, which is detrimental to coral. Experts also say that drug chemicals in the human body passed into the sea with urine can damage coral reefs by altering the balance of germs.
Sources :