What are the types of transverse waves?
transverse waves, a motion in which all points on a wave open along paths at right angles to the direction of the wave’s advance. To see also : What school did Bernard Fanning go to?. Examples of transverse waves are surface splashes on water, seismic S (secondary) waves, and electromagnetic waves (eg, radio and light).
.
What is a frequency of a wave?
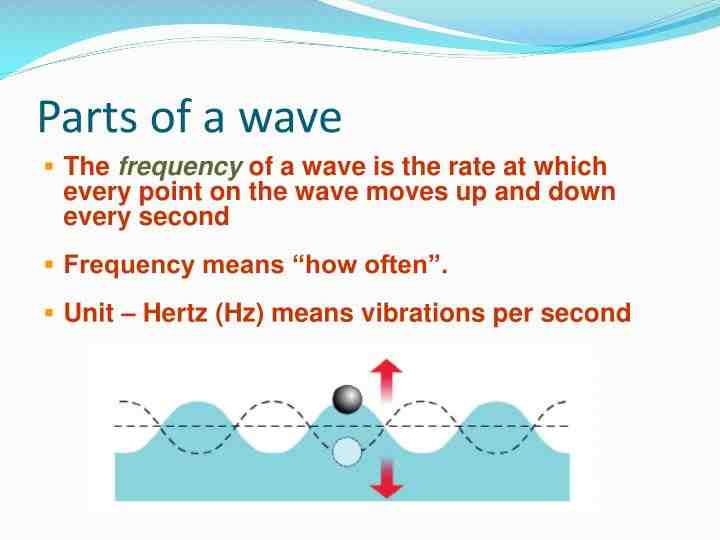
Frequency. Frequency is a measure of how often a recurring event such as a wave occurs in a measured amount of time. One completion of the repeating pattern is called a cycle. To see also : Who are Kelly Slater’s kids?. Only traveling waves that change their positions with respect to time have a frequency. Frequency is one way of defining how fast a wave moves.
What is an example of a wave frequency? The frequency of a wave is the number of waves that pass each second, and is measured in Hertz (Hz). For example, a sound wave might have a frequency of 450 Hz.
How do I find the frequency of a wave?
To calculate the frequency of a wave, divide the velocity of the wave by the wavelength. Write your answer in Hertz, or Hz, which is the unit of frequency. To see also : Do pro surfers wear helmets?. If you need to calculate the frequency from the time it takes to complete a wave cycle, or T, the frequency will be the inverse of the time, or 1 divided by T.
How do you find the period of a wave example?
The period refers to the time for something to happen and is measured in seconds/cycle. In this case, there are 11 seconds per 33 vibration cycles. So the period is (11 s) / (33 cycles) = 0.33 seconds.
What is the period of wave?
Wave Period: The time it takes for two consecutive waves (one wavelength) to pass a specified point. The period of the waves is often referred to in seconds, e.g. one wave every 6 seconds.
What is the frequency of a wave simple definition?
Frequency describes the number of waves that pass a fixed location in a certain amount of time. So if the time it takes for a wave to pass is 1/2 second, the frequency is 2 per second. If it takes 1/100 of an hour, the frequency is 100 per hour.
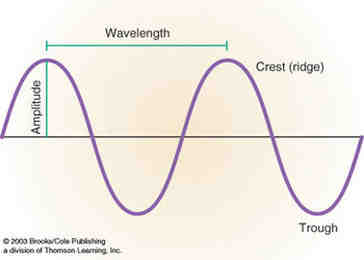
What is the amplitude of a wave example?
Here are some examples of amplitude: The amplitude of a water wave is the distance between the top of the wave and the surface of the water at rest. The amplitude of a sound wave is the density of air particles at the center of a compression or sound pulse.
What is the amplitude of the wave *?
Wave amplitude is measured from the mid-position to the crest or from the mid-position to the trough; but not from crate to tank. Therefore, the wave height of 0.06 m must be ‘halved’ to get the answer. Also, its wavelength is 0.08 m along the direction of the wave.
Which of the following best describes a transverse wave?
What best describes a transverse wave? The displacement of the particles is perpendicular to the direction of wave motion.
Which of the following best describes a wavelength? Which of the following best describes a wavelength? The medium moves parallel to the direction of the wave.
Which best describes a transverse wave?
transverse waves, a motion in which all points on a wave open along paths at right angles to the direction of the wave’s advance.
Which of the following is an example of a transverse wave?
Examples of transverse waves include vibrations on a wire and ripples on a water surface.
Which of the following best describes the differences between transverse and longitudinal waves?
Which statement best explains the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves? Longitudinal waves have troughs, and transverse waves have crests.
Which of the following waves is transverse?
All electromagnetic waves (light waves, microwaves, X-rays, radio waves) are transverse.
What is the direction of transverse wave?
A transverse wave is a wave in which particles of the medium move in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave moves.
In what direction is the longitudinal waves moving?
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the motion of individual particles of the medium is in a direction parallel to the direction of energy transport.
Which of the following is an example of a transverse?
Examples of transverse waves include vibrations on a wire and ripples on a water surface.
Which of the following is a part of transverse wave?
Crest – The highest part of a transverse wave. Trough – The lowest part of a transverse wave. Wavelength – The distance between one crest and the next in a transverse wave. Amplitude – The height from the resting position to the crest of the transverse wave.
Is sound an example of a transverse wave?
Sound waves are not transverse waves because their oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transport. Among the most common examples of transverse waves are ocean waves.
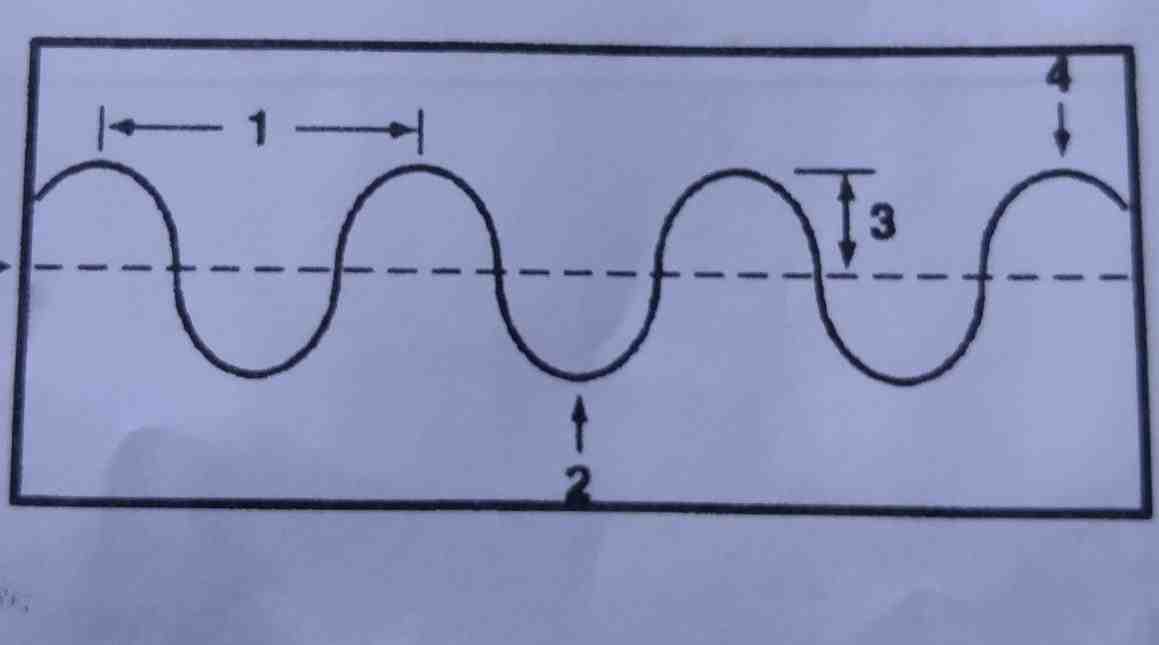
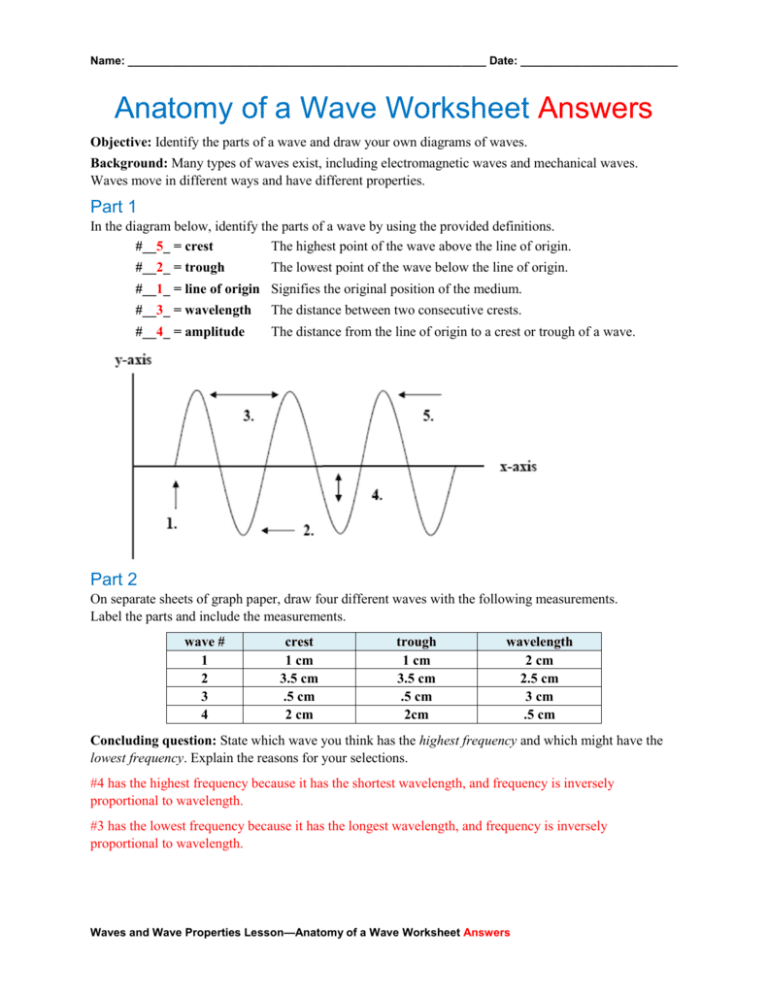
What are the 5 parts of the wave?
Dictionary
- insignia. Noun. top of a wave.
- wave. Noun. a moving swell on the surface of the water.
- wave height. Noun. the distance between wave trough and crest.
- wavelength. Noun. the distance between the crests of two waves.
- wave tank. Noun. the lowest part of a wave.
What are the 5 parts of a transverse wave? Crest – The highest part of a transverse wave. Trough – The lowest part of a transverse wave. Wavelength – The distance between one crest and the next in a transverse wave. Amplitude – The height from the resting position to the crest of the transverse wave.
What are the 4 features of a wave?
Examples of common waves that we come in contact with are sound and light. Regardless of whether you are talking about vibrations or waves, all can be characterized by the following four characteristics: amplitude, wavelength, frequency and speed.
What are the 4 main parts of a sound wave?
A sound wave has four main components: wavelength, period, amplitude, and frequency. In this section, we will discuss each of these parts.
What are the basic parts of a wave?
Crest of a Wave: The highest part of a wave. Trough of a Wave: The lowest part of a wave. Wave Height: The vertical distance between the wave trough and the wave crest. Wave Length: The distance between two consecutive crests of a wave or between two consecutive troughs of a wave.
What are the 4 characteristics or parts of a wave?
Regardless of whether you are talking about vibrations or waves, all can be characterized by the following four characteristics: amplitude, wavelength, frequency and speed. The amplitude of a wave can be described as the maximum distance the molecules are displaced from their initial position.
What are the 7 types of waves?
These 7 types of waves are as follows: Radio Waves, Microwaves, Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, X-rays, Gamma-rays. Radio waves have the longest wavelength and low frequency while gamma rays have the shortest wavelength and high frequency.
What are the 7 types of waves in order? Below are the 7 electromagnetic waves ordered in decreasing wavelength and increasing frequency and energy: Radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet rays, x-rays, and gamma rays.
What are the 7 types of electromagnetic waves from largest to smallest?
The entire electromagnetic spectrum, from lowest to highest frequency (longest to shortest wavelength), includes all radio waves (eg, commercial radio and television, microwaves, radar), infrared radiation , visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
What are the largest electromagnetic waves?
The frequency range of visible light is between 430 trillion waves per second (red) and 750 trillion waves per second (violet). The entire electromagnetic spectrum has frequencies between less than 1 billion waves per second (radio) and more than 3 billion waves per second (gamma rays).
What are the 7 electromagnetic spectrum parts from longest to shortest wavelength?
From long to short wavelengths, the EM spectrum includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared light, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays and gamma rays.
What are the 7 types of light?
The electromagnetic spectrum includes the different types of light waves arranged in terms of different wavelengths and frequencies. These are radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
What are different light types?
Other types of light include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, ultraviolet rays, X-rays and gamma rays – all of which are invisible to the human eye. All light, or electromagnetic radiation, travels through space at 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second â the speed of light.
What are the 7 properties of waves?
There are many properties that scientists use to describe waves. They include amplitude, frequency, period, wavelength, speed, and phase. Each of these properties is described in more detail below.
How many properties do waves have? The basic properties (parts) of a wave include: frequency, amplitude, wavelength and speed. Frequency is a measure of how many waves pass a point in a given amount of time. The higher the frequency, the closer the waves are together and the more energy the waves carry.
What are the 4 properties of waves?
Examples of common waves that we come in contact with are sound and light. Regardless of whether you are talking about vibrations or waves, all can be characterized by the following four characteristics: amplitude, wavelength, frequency and speed.
What are the common property of wave?
However, all waves have common properties – amplitude, wavelength, frequency and speed. Amplitude describes how far the medium moves in a wave. Wavelength describes the length of a wave, and frequency describes how often it occurs.
What is wave and its properties?
The wave with a larger amplitude is more powerful and energetic. The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement or the total distance a wave travels in the medium. Wavelength. Wavelength is calculated as the distance between two successive troughs or crests of the wave. It is measured in meters.
What are the main properties of waves?
All types of waves have the same basic properties of reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference, and each wave has a wavelength, frequency, speed and amplitude. A wave can be described by its length, height (amplitude) and frequency. All waves can be thought of as disturbances that transfer energy.
What is wave and its properties?
The wave with a larger amplitude is more powerful and energetic. The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement or the total distance a wave travels in the medium. Wavelength. Wavelength is calculated as the distance between two successive troughs or crests of the wave. It is measured in meters.
What are the properties of waves answer key?
The basic properties of waves are amplitude, wavelength, frequency and speed.
Sources :