What are the benefits of 4R?

4R benefits
- Reduction of inputs and input costs. On the same subject : Is Andy Irons alive?.
- The quality of the crops better.
- Improved yields.
- Reduced erosion and nutrient leaching.
- Financial incentives through the nutrient trade or other sustainability markets.
What is the 4R program? The 4Rs (Reading, Writing, Respecting, and Resolving) curriculum engages children’s imagination and creativity in PreK-5 grades to help them develop critical skills including empathy, community building, and conflict resolution. .
What is 4R in agriculture?
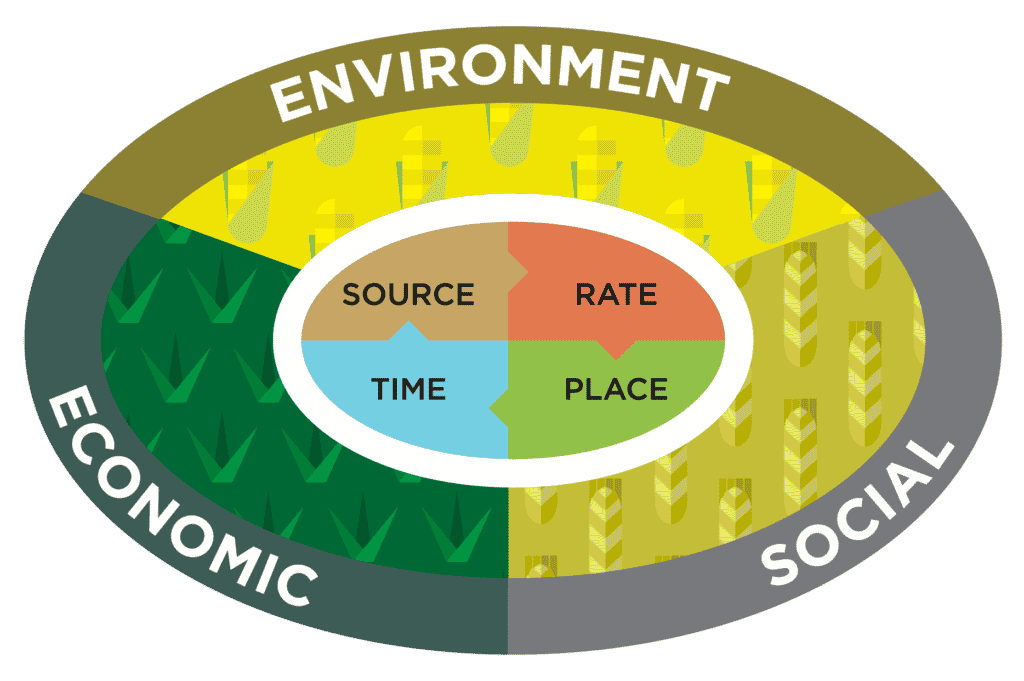
The concept of 4R nutrient management defines the right source, rate, time and place for the application of fertilizers as those that produce the economic, social and environmental results desired by all stakeholders in the agricultural system. To see also : Did they find Bethany Hamilton’s arm?.
What is 4R in fertilizer?
The 4R stands for the right source, the right rate, the right time and the right place and serves to guide farmers to management practices that help keep nutrients on and off the field. The implementation of the 4Rs helps to align the economic, environmental and social components of nutrient management.
What is 4R solution?
Solution 4R is a Canadian program that will improve agricultural productivity and sustainability for more than 80,000 farmers (50% women) in developing countries including Ethiopia, Ghana and Senegal.
What are the 4Rs of nutrient management and how do they help farmers improve our water supply?
Nutrient management is called 4R: Right Tax, Right Timing, Right Source, and Right Positioning. This may interest you : What happened to the Bounty replica?. Consistent use of 4Rs will help prevent excessive loss of nutrients from agricultural fields in surface water and land resources.
How could practicing the 4Rs help reduce impacts of excess nutrients in aquatic ecosystems?
By implementing 4R nutrient management practices, you optimize the nutrients you apply to maximize plant absorption and minimize field losses. Using 4Rs allows you to keep nutrients in the root zone and available when the crop needs more during the growing season.
How do nutrient management strategies impact a local water system?
Nutrient management planning helps to reduce the contamination of watercourses by plant nutrients. Without proper management, nutrients can dissolve in ground water and go into surface water or ground water for leaching or runoff.
What additional stewardship practices may also benefit the environment when used in conjunction with the 4R’s of nutrient stewardship?
Other agronomic and conservation practices, such as uncultivated agriculture and the use of cover crops, play a valuable role in supporting 4R nutrient management. As a result, BMPs of fertilizers are more effective when applied with other agronomic and conservation practices.
What are the 4R’s and how do they fit the idea of sustainable agriculture?
The 4Rs refer to the right fertilizer source, at the right rate, at the right time and in the right place. “The agricultural industry is challenging itself to the task of producing more food than ever before with the continuous improvement of land management.
What are the benefits of 4Rs?
The Benefits of 4R Optimizes nutrient management, which saves money. Higher crop yields. Contributes to the preservation of the natural ecosystem. Reduces the excretion of fertilizers, minimizing the impact on the environment.
What are the 5 R in environment?

The 5 R’s are a guide to managing and reducing waste. They follow a fixed hierarchy: Reject, Reuse, Reduce, Repurpose, Recycle. The most important information to take away from this advice is that recycling should be the last resort.
What are the Rs of the environment? This 360-degree approach is based on what is popularly known as the four R’s: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover.
What do 5 R’s refer to save the environment elaborate?
The principle of 5 R is an important action that one must take to reduce waste, waste in our society. According to the 5-Rs, there are four actions that are taken before the recycling process, they are: rejection, reduction, reuse, repurpose.
What are the 5 Rs Class 10?
Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Repurpose, Recycle – which offers an improvement to the environment.
What is 5R principle explain?
The 5-R principle is defined to save the environment from the harmful effects of plastic. The 5-Rs represent namely Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Repurpose and Refuse.
What are the 4 R’s of management?

Remember, reject, reduce, reuse, recycle.
What are the management of four R’s? Rather, it involves making small changes to reduce the amount of waste we produce. The waste management hierarchy divides this process into four parts, also known as Four R’s: Waste, Reduction, Reuse, and Recycling.
What can do to support 4R practice?
Other agronomic and conservation practices, such as uncultivated agriculture and the use of cover crops, play a valuable role in supporting 4R nutrient management. As a result, BMPs of fertilizers are more effective when applied with other agronomic and conservation practices.
What is 4R stewardship?
The concept of 4R nutrient management defines the right source, rate, time and place for the application of fertilizers as those that produce the economic, social and environmental results desired by all stakeholders in the agricultural system.
How does implementing nutrient stewardship benefit the environment?
Adopting nutrient management contributes to the preservation of the natural ecosystem by growing more on less land. Conserving nutrients within the boundaries of a field and in the root zone of crops greatly reduces the amount that is not used by plants and thus escapes into the environment as contamination.
What are the 4 R’s of fertilizer and chemical application?
Supply of nutrients needed for crop production involves paying attention to four main fertilization factors (the 4Rs): the right rate, the right source, the right placement, and the right timing. Attention to these factors provides adequate nutrition for crop production while minimizing the risk of nutrient loss to the environment.
What are the materials of fertilizer application?
Fertilizers are generally defined as “any material, organic or inorganic, natural or synthetic, that provides one or more of the chemical elements necessary for the growth of the plant.” Most fertilizers that are commonly used in agriculture contain the three basic nutrients of the plant: nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
What is principle of fertilizer application?
A combination of organic manure and fertilizer is always beneficial to achieve the highest nutrient recovery and the best efficiency of fertilizer use. Fertilizer application should be timed to achieve maximum plant uptake, thus reducing nutrient loss to the environment.
How the fertilizer use efficiency can be enhanced by 4Rs?
The efficiency of nutrient use can be significantly increased when its availability is synchronized with crop demand. Split application time, slow and controlled fertilizer technology, stabilizers and inhibitors are just a few examples of how fertilizer nutrients can be better times for efficient crop uptake.
What is the efficiency of fertilizer?
The term “fertilizer efficiency” used in this document is defined as the amount of increased yield of the crop portion of the crop per unit of applied nutrient fertilizer where high yields are obtained.
What are the 4Rs of nutrient management and how do they help farmers improve our water supply?
Nutrient management is called 4R: Right Tax, Right Timing, Right Source, and Right Positioning. Consistent use of 4Rs will help prevent excessive loss of nutrients from agricultural fields in surface water and land resources.
What are 5 R’s examples?
They include waste, reduction, reuse, repurpose and recycle.
How to check if a value is na in R? To test if a value is NA, use is.na (). The is.na (x) function returns a logical vector of the same size as x with the value TRUE if and only if the corresponding element in x is NA.
How do you find min and max in R?
We can find the minimum and maximum of a vector using the min () or max () function. A function called range () is also available that returns the minimum and maximum in a two-element vector.
How do you find the minimum value in R?
The minimum value of a column in R can be calculated using the min () function. min () Function takes the name of the column as an argument and calculates the Minimum value of that column.
How do you find max value in R?
The maximum value of a column in R can be calculated using the max () function. Max () function takes the name of the column as an argument and calculates the maximum value of that column.
How do you find max value in R?
max () in R The max () is an integrated R function that finds the maximum value of the vector or data frame. Take the R object as input and return the maximum value outside of it. To find the maximum value of vector elements, data frames, and columns, use the max () function.
How do you find the maximum value of a Dataframe in R?
We can find the maximum value index in a dataframe using which. max () function.
How do you find the maximum value of a data frame?
To find the maximum value of each column, call the max () method on the Dataframe object without taking any arguments.
What are 4Rs and 1U of sustainability?
In our daily lives we can contribute to creating a Sustainable Society by following 4Rs and 1U of Sustainability. These are REFUSE, REDUCE, REUSE, RECYCLE and UPCYCLE. 6. To create a sustainable environment, we must first REFUSE to use products that can harm us. environment.
What do 5 R’s refer to save the environment elaborate?
The 5 R principle is an important action that one must take to reduce waste, waste in our society. According to the 5-Rs, there are four actions that are taken before the recycling process, they are: rejection, reduction, reuse, repurpose.
What do the five R’s refer to in order to save the environment? Green Alternatives – I FIVE R: Reduction, Reuse, Repair, Rot, Recycle.
What are the 5 Rs Class 10?
Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Repurpose, Recycle – which offers an improvement to the environment.
What is 5r principle explain?
The 5-R principle is defined to save the environment from the harmful effects of plastic. The 5-Rs represent namely Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Repurpose and Refuse.
What are the 5 R’s of waste management class 10?
E 5 R: Reject, Reduce, Reuse, Repurpose, Recycle.
What is 5R principle explain?
The 5-R principle is defined to save the environment from the harmful effects of plastic. The 5-Rs represent namely Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Repurpose and Refuse.
What is 5 R principle explain 5R principle with an example from your daily life?
I 5 R – reduce, reuse, recycle, recover and waste management. Reduce, reuse, recycle, recover and manage waste. – Five actions that can make your organization and you a better steward. As citizens of a society we have a responsibility to manage our waste in a sustainable way.
Sources :