What should you not take with methadone?
Drugs you should not use with methadone Pentazocine, nalbuphine, butorphanol, and buprenorphine. These drugs may reduce the pain-relieving effects of methadone. To see also : Who is Andy’s wife?. This can cause withdrawal symptoms.
Does orange juice interfere with methadone? If you regularly eat grape or grape juice, you should be monitored for side effects and / or changes in methadone levels. Do not increase or decrease the amount of grapefruit products in your diet without first talking to your doctor. Orange juice is not expected to interact.
Can you take other medications with methadone?
If certain other medications are taken during your methadone treatment, you may be at risk of developing serious, life – threatening side effects, such as breathing problems, sedation, or coma. On the same subject : Do surfers run into each other?.
What medications can be taken with methadone?
| Classification of Medicine | Examples | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | rifampicin | Induction of methadone metabolism |
| Reverse Inhibitors -Non-Nuclear Transducer | effective, nevirapine | |
| Azole antifungals | fluconazole, ketoconazole | Inhibition of methadone metabolism |
| Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors | fluoxetine |
What medications you Cannot take with methadone?
Interactions that can make your drugs less effective
- Anticonvulsants such as pheniobarbital, phenytoin, and carbamazepine. These drugs can cause methadone to work. …
- HIV drugs such as abacavir, darunavir, efavirenz, nelfinavir, nevirapine, ritonavir, and telaprevir. …
- Antibiotics such as rifampin and rifabutin.
What pain medication can you take while on methadone?
Methadone and pain relief This means that if you are in pain, you need pain medication as much as anyone else in a similar situation. To see also : What does glassy mean in surfing?. For example, if you have headaches, menstrual cramps or any other low-level pain, you should get relief with a normal dose of codeine-free aspirin or Tylenol.
Can you treat pain with methadone?
What Does Methadone Do? Methadone changes the way your brain and nervous system respond to pain so that you feel relieved. Its effects are slower than those of other strong painkillers like morphine. Your doctor may prescribe methadone if you have severe pain due to a long-term injury, surgery or illness.
Can you take traMADol while on methadone?
Methadone in combination with traMADol can lead to serious side effects, including seizures, respiratory distress, coma, and even death. Combined use can also increase the risk of potentially serious and potentially life – threatening irregular heart rhythms, although it is a relatively rare side effect.
How do you maximize methadone?
The daily dose of methadone should then be increased by 5-10 mg every few days, as needed, to reduce cravings for opioids and illicit use of opioids. The dose should not be increased more than 20 mg per week. Patients should be reviewed before each dose increase. The average effective dose of methadone is 60-120 mg.
Is 100 milligrams of methadone a lot?
“The current study provides strong evidence that we can achieve much better results at much higher dose rates than 50 mg per day,” says Dr. Strain. Doses in excess of the current control limit of 100 mg per day may provide the best outcome for some patients, said Dr.
What is considered high doses of methadone?
However, current federal regulations in the United States discourage methadone doses greater than 100 mg / d. Well-conducted clinical trials to test such high doses are likely to be required to support a review of these regulations.
What class does methadone fall under?
Methadone belongs to a class of drugs called opioid analgesics.
Is methadone opioid or opiate? Methadone is a synthetic opioid agonist that eliminates withdrawal symptoms and exacerbates drug cravings by acting on opioid receptors in the brain – the same receptors that activate other opioids such as heroin, morphine, and opioid pain medications.
What is the classification for methadone?
Methadone is in a class of medicines called opioid analgesics (narcotics).
Is methadone a narcotic yes or no?
Methadone is a synthetic (man-made) narcotic. It is legally used to treat narcotic addiction and to alleviate severe pain, often in individuals with cancer or terminal illnesses. Although methadone has been legally available in the United States since 1947, it has recently emerged as an abusive drug.
What is an opioid classification?
All opioids are controlled substances. 2. According to the CSA, the classification of opioids ranges from Schedule I to Schedule V, depending on whether they are approved for medical use, their risk of abuse, and the likelihood of developing physiological dependence.
Is methadone considered a psychotropic medication?
Methadone is currently scheduled as a “narcotic drug”, which falls under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs and buprenorphine as a “psychotropic substance”, which falls under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances.
What are the examples of psychotropic substances?
Examples of psychotropic substances include alcohol, caffeine, nicotine, marijuana, and certain pain medications. Many illegal drugs, such as heroin, LSD, cocaine, and amphetamines, are also psychotropic substances.
Is methadone considered a medication?
Methadone is a medication approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) as a medication-assisted treatment (MAT), as well as for pain management. When taken as prescribed, methadone is safe and effective.
Is methadone a narcotic yes or no?
Methadone is a synthetic (man-made) narcotic. It is legally used to treat narcotic addiction and to alleviate severe pain, often in individuals with cancer or terminal illnesses. Although methadone has been legally available in the United States since 1947, it has recently emerged as an abusive drug.
What class of medication is methadone?
Methadone is a medication used to treat Opioid Depression (OUD). Methadone is a long-acting total opioid agonist, and a schedule II controlled medication.
Is methadone a stimulant or opioid?
Methadone is part of a category of drugs called opioids. It was invented by German doctors during World War II. When it came to the United States, doctors used it to treat people with severe pain. Today, you might get it as part of a treatment program for heroin addiction or narcotic painkillers.
What are Schedule 3 drugs examples?
Some common drugs in schedule class 3 include:
- Ketamine.
- Anabolic steroids.
- Buprenorphine (Suboxone)
- Codeine and hydrocodone products mixed with aspirin or acetaminophen.
- Official list of Schedule 3 drugs.
What are Schedule 3 drugs in Australia? Schedule 3 contains substances and preparations for therapeutic use that are substantially safe in use but require the advice, management or monitoring of a pharmacist. The use of Schedule 3 requires only an initial medical diagnosis and does not require intensive medical management.
What makes a drug schedule 3?
The drug has less potential for abuse than the drugs in schedules 1 and 2. The drug has currently taken up medical use in treatment in the United States. Drug abuse can lead to moderate or low physical dependence or high psychological dependence.
Is the INCB part of the UN?
While 13 Board Members are independent, the Secretariat, officials and staff of the INCB are entrusted to the United Nations.
What does the INCB do?
The INCB aims to oversee the implementation of international drug conventions, ratified by UN member states. International drug laws aim to restrict the illicit production and use of harmful opioid substances and to ensure appropriate access to opioid formulations for clinical and scientific purposes.
What is a Schedule 3 opioid?
Schedule III, IV & V Opioids Buprenorphine is a Schedule III drug, and all drugs containing Buprenorphine, such as Suboxone. Codeine with aspirin or Tylenol, a Schedule III drug. Cough medicines including codeine, which are Schedule V drugs. Tramadol, a Schedule IV drug.
What drugs are narcotics?
Control is in place for 136 narcotic drugs, mainly natural products such as opium and its derivatives, morphine, codeine and heroin, but also synthetic drugs, such as methadone and pethidine, as well as cannabis and coconut leaf.
What is the mechanism of action of narcotic drugs?
Summary. Opioid drugs, defined by morphine, produce their pharmacological actions, including analgesia, by acting on receptors located on the membranes of neuronal cells. Its major effect on the nervous system is thought to be the presynaptic action of opioids to inhibit neurotransmitter release.
What drug class is buprenorphine?
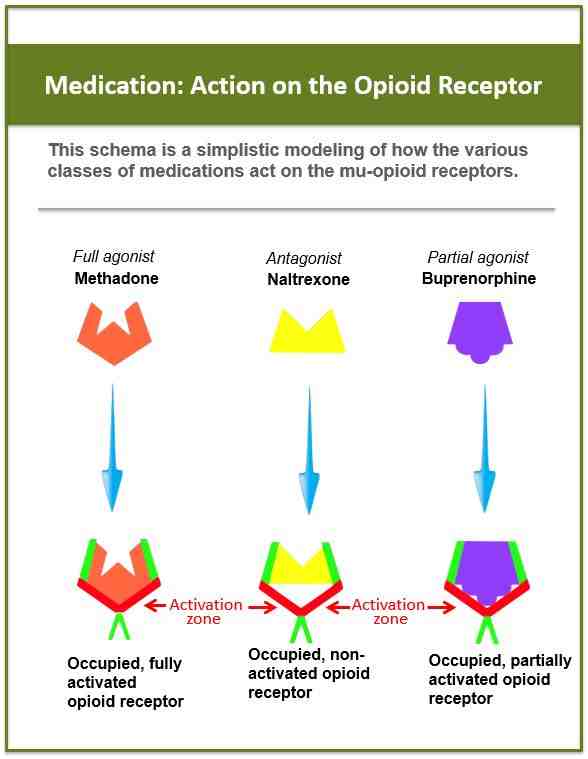
Buprenorphine is in a class of medications called opioid partial agonist-antagonists and naloxone is in a class of medications called opioid antagonists.
What is considered buprenorphine? Buprenorphine is the active drug in buprenorphine / naloxone. Buprenorphine is called a partial opioid agonist, which means it works partially as an opioid and the effect is weaker than total agonists like heroin and methadone.
Why is buprenorphine a narcotic?
The drug has high affinity and slow dissociation from mu-opioid receptors and may temporarily block other opioids. Because of this high affinity, buprenorphine displaces opioids from the mu receptor, leading to recent withdrawal of patients who have used opioids.
Is buprenorphine a pure opioid?
Although buprenorphine is an opioid, the mu-opioid receptor has only partial analgesic activity. The two reasons buprenorphine has no use as an analgesic is that it is only a partial agent and has a capping effect.
What kind of opioid is in buprenorphine?
Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agent. This means that, like opioids, it produces effects such as euphoria or respiratory depression. With buprenorphine, however, these effects are weaker than those of whole drugs such as heroin and methadone.
What kind of opioid is in buprenorphine?
Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agent. This means that, like opioids, it produces effects such as euphoria or respiratory depression. With buprenorphine, however, these effects are weaker than those of whole drugs such as heroin and methadone.
What is the main ingredient in buprenorphine?
Each sublingual tablet contains 8 mg of buprenorphine (as buprenorphine hydrochloride). Discharges with a known effect: Each tablet contains 175.6 mg of lactose monohydrate and 0.76 mg of sunset yellow (E110).
Is buprenorphine a pure opioid?
Although buprenorphine is an opioid, the mu-opioid receptor has only partial analgesic activity. The two reasons buprenorphine has no use as an analgesic is that it is only a partial agent and has a capping effect.
What controlled class is buprenorphine?
Controlled Status: Bopporphine and all products containing bupnephorin are regulated in schedule III of the Controlled Substances Act.
What controlled substance is Subutex?
Buprenorphine, a controlled substance sold under the brand names Subutex and Suboxone, is a medication for the treatment of opioid use disorders.
Is Suboxone a Class 2 or 3?
Safety and efficacy in patients under 18 years of age have not been established (1 – 7). Bunavail, Cassipa, Probuphine, Sublocade Injection, Suboxone, Zubsolv, and bublingrenpine sublingual tablets are one Schedule III narcotics with one indication, maintenance treatment of opioid dependence.
Is gabapentin an opioid?
Gabapentin is not a narcotic. It is not classified as a controlled substance in most states. (Kentucky, West Virginia, Michigan, Tennessee, and Virginia have reclassified gabapentin as a Schedule V controlled substance). Gabapentin is not an opioid.
Is gabapentin opiate or narcotic? Official Answer. The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is not currently considered by the federal government as a narcotic substance or controlled by the federal government, but some states have enacted legislation so that the drug is treated as one or monitored by a drug monitoring program. state prescription.
What drug class is gabapentin under?
Gabapentin is in a class of medications called antidepressants. Gabapentin treats seizures by reducing abnormal excitement in the brain. Gabapentin alleviates PHN pain by altering the way the body perceives pain.
Is gabapentin a controlled substance 2020?
Gabapentin control status and monitoring in selected states as of November 20, 2020 States where gabapentin is classified as a controlled substance (AL, KY, MI, ND, TN, VA, and WV).
Is gabapentin an opioid or benzo?
The drug, which is not opioid or not designated as a controlled substance by federal authorities, is used to treat nerve pain. But the board found that it was the most prescription medication on its list that month, surpassing oxycodons by more than 9 million doses.
Is gabapentin a high drug?
Gabapentin can produce feelings of relaxation, relaxation and euphoria. Some users have reported that the high level of snorted gabapentin can be like a stimulant. It may also contribute to the euphoric effects of other drugs, such as heroin and other opioids, and the risks are likely to increase when taken in this way.
Is gabapentin a strong opioid?
Gabapentin is not an opiate drug and is not considered a dangerous abuse drug like most opiate drugs.
Is gabapentin considered an addictive drug?
Yes, Gabapentin can be addictive. Many people use gabapentin for legitimate medical conditions, but some people become addicted to the drug and may abuse it. Frequent use of gabapentin can lead to physical dependence on the drug.
Is there opioid in methadone?
Methadone is a long-acting total opioid agonist, and a schedule II controlled medication.
Are methadone narcotic or not? Methadone is a synthetic (man-made) narcotic. It is legally used to treat narcotic addiction and to alleviate severe pain, often in individuals with cancer or terminal illnesses. Although methadone has been legally available in the United States since 1947, it has recently emerged as an abusive drug.
Is methadone a full opioid?
Methadone is a medication used to treat Opioid Depression (OUD). Methadone is a long-acting total opioid agonist, and a schedule II controlled medication.
Is methadone a type of opioid?
Methadone is a long-acting opioid drug used to replace short-acting opioids that may be addictive, such as heroin, oxycodone, fentanyl or hydromorphon.
What is full opioid?
Opioids are a total agonist of the opioid receptors in the brain and result in the full opioid effect. Examples of total agonists are heroin, oxycodone, methadone, hydrocodone, morphine, opium and others.
Sources :